Vendor Integrations Break with GDAP: The Fix!
In October of last year, I published an article explaining how GDAP breaks vendor integrations: Vendor Integrations will Break with GDAP – (tminus365.com)
This is specifically for Vendors using an integration that leverages delegated access into downstream customer tenants. If you are a vendor that requires consent to your integration at a per tenant level, this article does not apply to you. This article will have many similar prerequisite steps that I outlined here: My Automations Break with GDAP: The Fix! – (tminus365.com)
This previous article outlines how an MSP can continue to leverage internal automations with GDAP. In this article, I will be outlining the steps for a Microsoft CSP Partner/MSP and vendor to take in order for integrations to work with GDAP. Note that if these steps are not taken, your integration will break.
Timelines As of the writing of this article 5/4/2023, Microsoft states that will begin auto-transitioning relationships to GDAP starting May 22, 2023. If this timeline holds true, this is when I believe many people will be reading this article, as their automations will stop working. Get ahead of this now!
Consulting If you would like some more targeted consulting as it relates to these changes, please reach out to me at [email protected]
Why do my integration break?
Accessing tenants as a Microsoft partner has traditionally been done with Delegated Access Permissions or DAP. DAP provides you Global Administrator access to all of the downstream tenants. Whenever you set up an app registration using the Secure Application model, you would add that service principal to the Admin Agents group in Partner Center. By doing so, you were able to generate refresh tokens and access tokens into all of your customer environments. We have been leveraging this model for years now to create automation workflows. This model of consent is known as a “pre-consent” since there were no additional steps you needed to take in order to leverage the app registration in these tenants.
Shifting to GDAP, the core benefit is the additional layers of security provided to help protect yourself and your downstream customers against supply chain attacks. As part of the shift to this new model, the “pre-consent” concept is no longer in play. We now need to take additional steps to consent for applications in our downstream customer tenants. The good news is that this can still be done in bulk using an “on-behalf of” consent model, meaning you do not need to grant consent to your application registration on a per customer basis. The bad news is that it now requires many more additional steps and gets confusing. Hence this article 😊
MSP/Partner Prerequisite Steps
Here I will outline what you need to direct the MSP/Partner to do in their own environment in order for your integration to support GDAP.
Create a Service Account for the Integration
The first thing to do is set up a new service account for your integration. The format could be something like <YourCompany>@mspdomain.com. I think it is important to have a dedicated account here so that nothing breaks over time if you have users leaving the partner organization. As a best practice, do not use a regular user account for your integrations. Here are some requirements for this service account:
They need to be a Global Administrator initially. We will need this service account to have the GA role when we acquire access tokens in future steps. This user does not need to have perpetual GA rights so it is recommended to leverage Privileged Identity Management (PIM) so that you can make this user eligible for the role when you need it and reduce your attack surface.
This user requires MFA. This can be enforced through Conditional Access or Per User MFA settings. This MFA has to be with Microsoft and cannot be from a 3rd party like Duo
This user needs to be added to the Admin Agents group in Azure AD
Important! If possible, direct the MSP to leverage a documentation tool like IT Glue or Hudu to store the MFA token and password for this user so that it can be accessed by more than one person if needed.
Configuring GDAP Relationships
Another prerequisite is that the partner has added a GDAP relationship for all of their customers.
If you are not familiar with GDAP, check out my other blog post:
The roles scoped as part of those relationships is very important. There are two major concepts that you have to consider:
In order to leverage the on-behalf consent model to grant your application rights to downstream customer environments, we need the relationship to have one of the following Azure AD roles:
Global Admin
Privilege Role Admin
Cloud Application Admin
Additionally, in order to make specific API calls, the GDAP relationship needs to include roles that would encompass those permissions. i.e. if you added a permission for your integration to read configuration profiles in Intune, you would need the Intune Administrator role as part of the GDAP relationship.
This means you need to direct the MSP/Partner for the roles that they need to have as part of their GDAP relationships with customers.
The other key step partners need to take with GDAP relationships is to assign a Security group for the GDAP relationship that includes the service account we created in the first step as a member. The partner could create a Security group specific to your integration or they could leverage an existing security group. In my use case, I created a group called GDAP_SG1 and added my service account as a member:
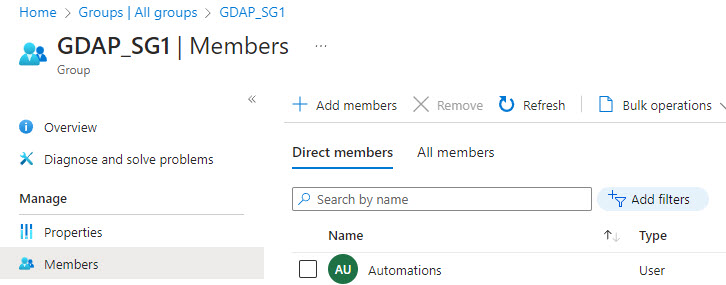
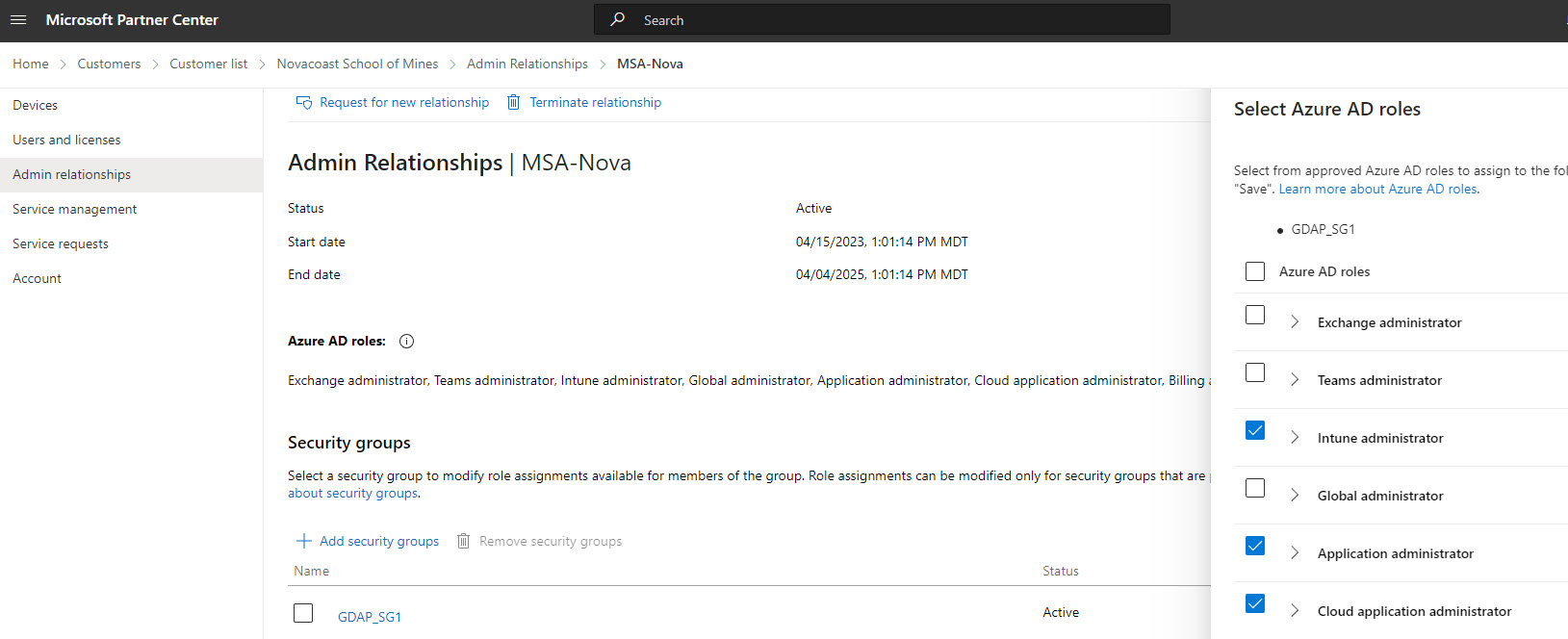
In Partner Center, the partner will need to ensure that this security group is assigned to each GDAP relationship and has at least one of the following permissions:
Global Admin
Privilege Role Admin
Cloud Application Admin
Vendor Action Items
Whether you have an existing integration or are creating a new one, you will need the MSP/Partner to follow the steps above. Your steps are as follows:
Build a workflow that leverages the Secure Application Model to acquire access tokens for the MSP/Partners environment.
Leverage the consent API to consent to your integration for the partner’s downstream customers.
Secure Application Model Flow
Your app will need to support a front-end that can walk an MSP/Partner through the Secure Application Model Process. Enable secure application model – Partner app developer | Microsoft Learn
During this flow you will want to programmatically do the following:
Create an App Registration in the Partners Tenant
Create and store the app registration Secret Key, Client ID, and Partner Tenant ID
Generate and store a refresh token
In this flow, the partner will be using the service account created in the previous section. The permissions you add should be everything that your integrations need to work.
Get Downstream Customers
Consent On-behalf
Microsoft has created an API to consent on-behalf of downstream customers vs needing to consent to an application one customer at a time.
Control Panel Vendor APIs for customer consent – Partner app developer | Microsoft Learn
You will use an access token generated from the application registration created in the Partners tenant with the Secure Application model. In the body, you will pass in the application ID, Application Name, and a list of all of the application grants part of your integration. Ex:
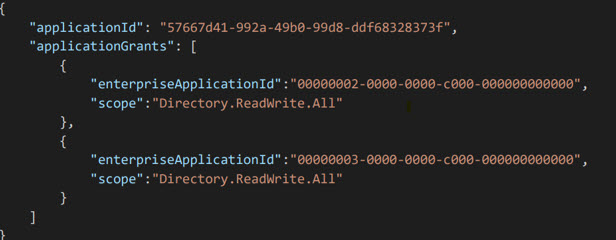
Each enterprise applciation ID represents a particular workload in Microsoft. Its likely you will mostly be interacting with the Graph API workload. Here are the workload IDs:

Once this is complete, you will be able to acquire access tokens into downstream customer environments and make API calls for that tenants information. (Like you might already be doing today).
Updating Permissions
Additional Considerations
Security Considerations
If you are a vendor (not providing any self-hosting capabilities), it is extremely important that you manage the secrets for the application in a very secure fashion. Encryption at rest and in transit are table stakes. If these secrets or refresh tokens were to get breached, an attacker could leverage the same workflow you use for your integration to cause damage in downstream customer environments. Their access would be limited to the permissions scoped by your integration and what GDAP roles the service account has access to so its not as much of a widespread security concern as what we have today with DAP but still warrants the highest levels of attention in my opinion.
Consent on behalf: Pros and Cons
I think as a vendor and as an MSP, you need to strongly consider the Pros and Cons of using the on behalf of consent model I described in this article vs consenting on a per tenant level
Pros:
As a vendor and MSP, your onboarding time for getting all customers integrated is significantly reduced. We are talking about having to login with each customer you want to integrate (per tenant) vs having all of that automated through a setup wizard and only having to sign in with one account.
As a vendor, if you ever updated your permissions, you can automate the consent across customers vs having to ask the partner to reconsent across all customers again.
Cons:
As a vendor and MSP, you have to perform all of the prerequisite steps for GDAP that I outlined here and make sure that the GDAP relationship includes permissions needed for the integration. If you just did per tenant consent, you do not have to worry about GDAP at all. At the end of the day, this could provide a much better customer experience and less helpdesk calls.
As a vendor, you have a lot more overhead to worry about to support this configuration. This includes storing many more secrets, creating a specific workflow to set up the secure application model, refreshing tokens, and having a job that can run the consent API.
Helpful Resources
Last updated